Azure Attribute-based Access Control (ABAC)
As an organization expands, the number of role assignments increases to implement more precise access control. With the addition of Attribute-based access control, we can reduce the role assignments and use conditions to restrict access to resources and grant access based on business requirements.
Attribute-based Access Control (ABAC) is a authorization method that defines access levels based on attributes of security principals, resources, and requests. ABAC allows granting access to a resource based on conditions expressed as predicates using these attributes. Azure ABAC extends Azure Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) by adding conditions to role assignments, enabling authorization based on principal, resource, and request attributes.
This condition is expressed as a predicate using attributes associated with any of the following:
- Security principal that is requesting authorization
- Resource to which access is being requested
- Parameters of the request
Currently available for:
- Standard storage accounts
- Azure Blob Storage
- Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2
- Azure Queues
Uses:
- Request and resource attributes for access control
Not yet available for:
- Other storage performance tiers and resource types
For more information:
In this guide, you will learn how to limit access to blobs based on a specific tag. For instance, you will add a condition to a role assignment so that Test user can only read files marked with the tag “Project=Prod”
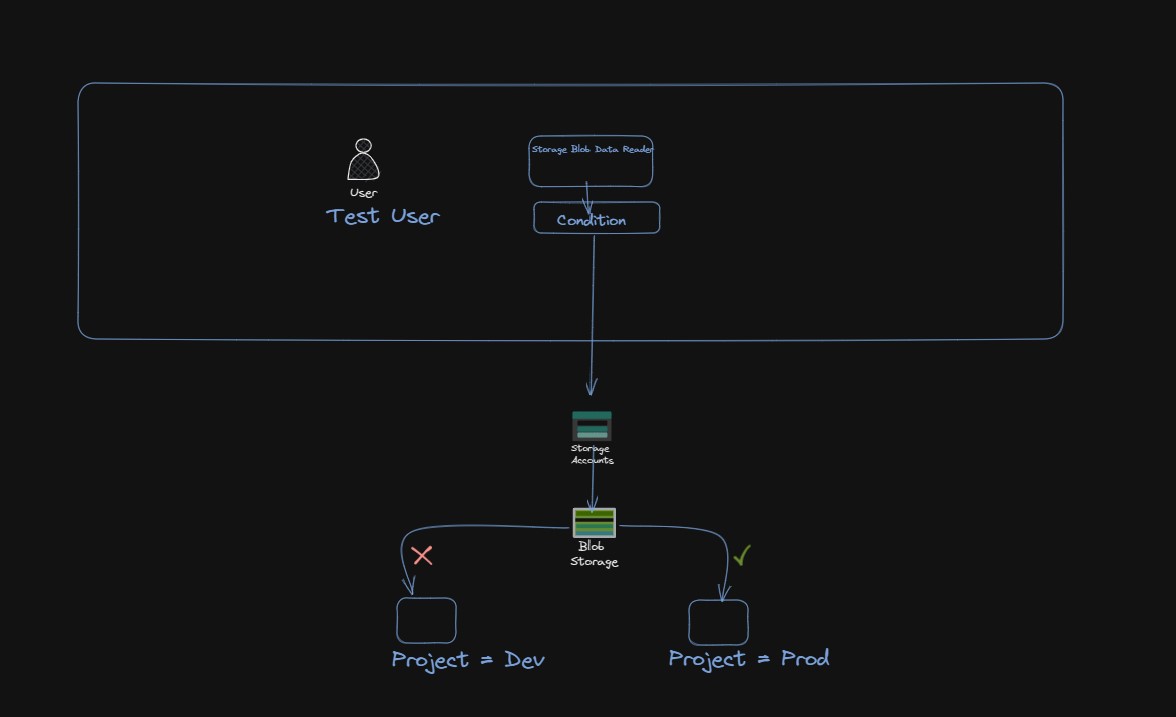
We will use Powershell to Create resources . However I will add the screenshot of the Role Condition Action Pane from Azure Portal.
If we express the condition in code, it will look like following.
(
(
!(ActionMatches{'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/read'}
AND NOT
SubOperationMatches{'Blob.List'})
)
OR
(
@Resource[Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/tags:Project<$key_case_sensitive$>] StringEquals 'Prod'
)
)
Upload new blob with index tags
Connect-AzAccount
$storageAccountName = "sc100lstorage" #Update with your storage account name
$containerName = "sc100container" #Update with your blob container name
$resourceGroup = "SC-100Lab" #Update with your resource group name
$file1 = "$pwd\file1.txt"
$file2 = "$pwd\file2.txt"
#Upload a blob by using the Set-AzStorageBlobContent command. Set tags by using the -Tag parameter.
$storageAccount = Get-AzStorageAccount -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroup -AccountName $storageAccountName
$ctx = $storageAccount.Context
Set-AzStorageBlobContent -File $file1 -Container $containerName -Context $ctx -Tag @{"Project" = "Prod";}
Set-AzStorageBlobContent -File $file2 -Container $containerName -Context $ctx -Tag @{"Project" = "Dev";}
Assign a Storage Blob Data reader role with a condition to User
#Initialize the Storage Blob Data Reader role variables.
$roleDefinitionId = '2a2b9908-6ea1-4ae2-8e65-a410df84e7d1'
#Initialize the scope for the resource group.
$scope = "/subscriptions/$subscriptionId/resourceGroups/$resourceGroup"
#Initialize the condition.
$condition = "((!(ActionMatches{'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/read'} AND NOT SubOperationMatches{'Blob.List'})) OR (@Resource[Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/tags:Project<`$key_case_sensitive`$>] StringEquals 'Prod'))"
$conditionVersion = '2.0'
$description = 'Read access to blobs with the tag Project=Cascade'
$userObjectId = Get-AzADUser -UserPrincipalName $userUPN | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Id
#Use New-AzRoleAssignment to assign the Storage Blob Data Reader role with a condition to the user at a resource group scope.
New-AzRoleAssignment -ObjectId $userObjectId -Scope $scope -RoleDefinitionId $roleDefinitionId -Description $description -Condition $condition -ConditionVersion $conditionVersion
View the condition in the Azure portal
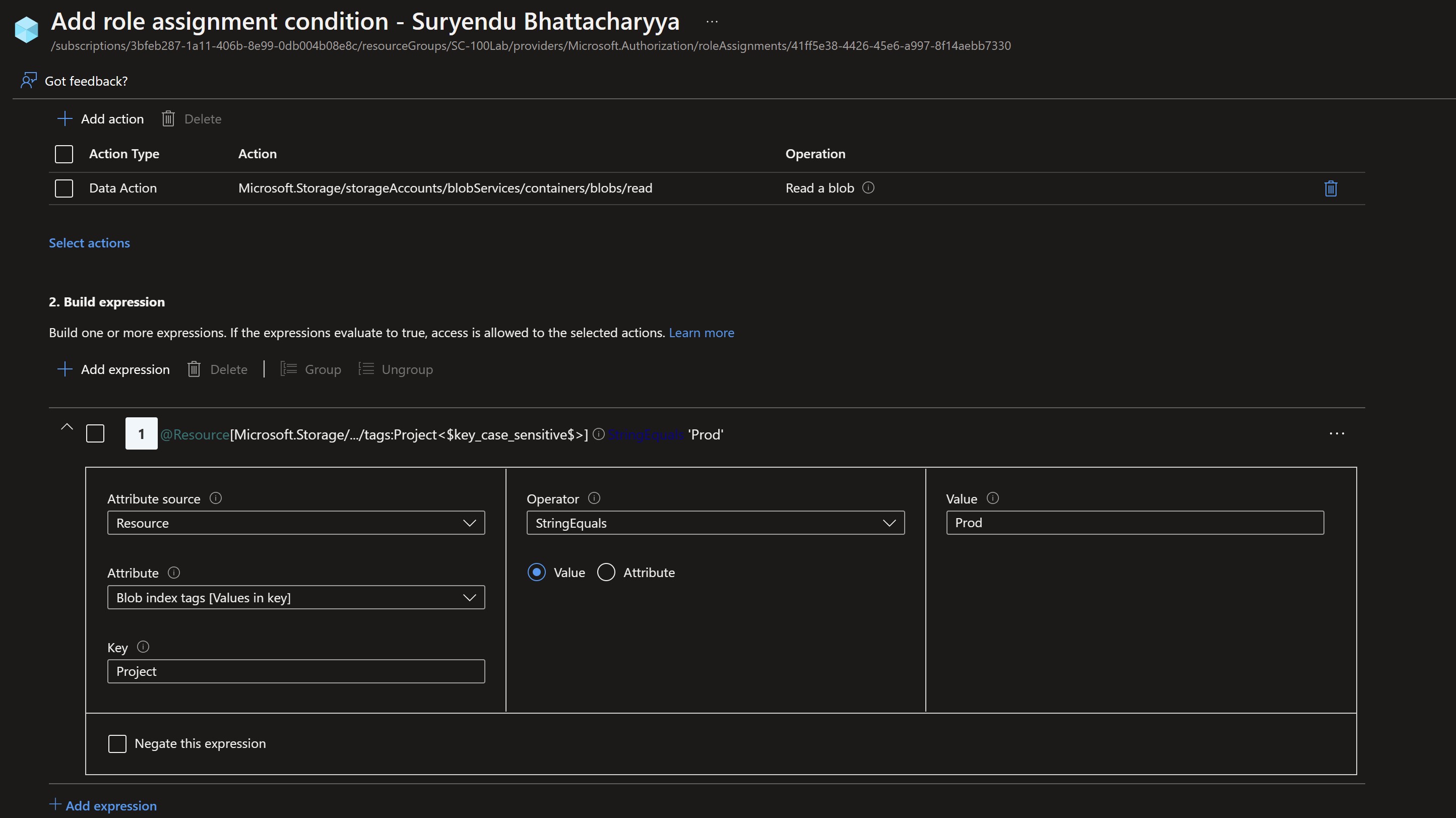
Test the condition
Notice you will not be able to read the file2.txt.
#Open a new PowerShell window.
#Use Connect-AzAccount to sign in as Test user.
Connect-AzAccount
# Initialize the following variables with the names you used.
$storageAccountName = 'sc100lstorage' #Update with your storage account name
$containerName = 'sc100container' #Update with your blob container name
$ctx = New-AzStorageContext -StorageAccountName $storageAccountName
# Use Get-AzStorageBlob to try to read the file for the Prod and Dev project.
Get-AzStorageBlob -Container $containerName -Blob file1.txt -Context $ctx
Get-AzStorageBlob -Container $containerName -Blob file2.txt -Context $ctx
You will get the following output when accessing file2.txt. User will be able to access file1.txt.
Get-AzStorageBlob -Container $containerName -Blob file2.txt -Context $ctx
Get-AzStorageBlob : Service request failed.
Status: 403 (This request is not authorized to perform this operation using this permission.)
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
x-ms-request-id: 605f7e19-f01e-0039-67f6-3a7230000000
x-ms-client-request-id: 71f37aff-a553-4106-86e2-f96786a15e1f
x-ms-version: 2021-06-08
x-ms-error-code: AuthorizationPermissionMismatch
Date: Tue, 07 Feb 2023 13:19:12 GMT
Server: Windows-Azure-Blob/1.0 Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0At line:1 char:1
+ Get-AzStorageBlob -Container $containerName -Blob file2.txt -Context ...
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : CloseError: (:) [Get-AzStorageBlob], RequestFailedException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : RequestFailedException,Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Commands.Storage.Blob.Cmdlet.GetA
zureStorageBlobCommand